Releases: JohnSnowLabs/spark-nlp
Spark NLP 6.0.1: SmolVLM, PaliGemma 2, Gemma 3, PDF Reader enhancements
📢 Spark NLP 6.0.1: Introducing New State-of-the-Art Vision-Language Models and Enhanced Document Processing
We are pleased to announce the release of Spark NLP 6.0.1, bringing exciting new vision features and continued enhancements. Expand your NLP capabilities at scale for a wide range of tasks by upgrading to 6.0.1 and leverage these powerful new additions and improvements!
We also have been adding blog posts covering various examples for our newest features. Check them out at Medium - Spark NLP!
🔥 Highlights
- Added support for several new State-of-the-Art vision language models (VLM) including Gemma 3, PaliGemma, PaliGemma2, and SmolVLM.
- Introduced new parameter options for the PDF Reader for enhanced document ingestion control.
🚀 New Features & Enhancements
New VLM Implementations
This release adds support for several cutting-edge VLMs, significantly expanding the range of tasks you can tackle with Spark NLP:
- Gemma 3: The latest version of Google's lightweight, state-of-the-art open models. (link to notebook)
- PaliGemma and PaliGemma 2: Integration of the original PaliGemma vision-language model by Gogle. This annotator can also read PaliGemma2 models. (link to notebook)
- SmolVLM: small, fast, memory-efficient, and fully open-source 2B VLM (link to notebook)
PDF Reader Enhancements
The PDF Reader now includes additional parameters and options, providing users with more flexible and controlled ingestion of PDF documents, improving handling of various PDF structures. (link to notebook)
You can now
- Add
splitPageparameter to identify the correct number of pages - Add
onlyPageNumparameter to display only the number of pages of the document - Add
textStripperparameter used for output layout and formatting - Add
sortparameter to enable or disable sorting lines
🐛 Bug Fixes
This release also includes fixes for several issues:
- Fixed a python error in
RoBERtaMultipleChoice, preventing these types of annotators to be loaded in Python - Fixed various typos and issues in our Jupyter notebook examples
❤️ Community Support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas, and show off how you use Spark NLP!
- Medium Spark NLP articles
- JohnSnowLabs official Medium
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
⚙️ Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==6.0.1
Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:6.0.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:6.0.1
GPU
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:6.0.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:6.0.1
Apple Silicon
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:6.0.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:6.0.1
AArch64
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:6.0.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:6.0.1
Maven
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp_2.12</artifactId>
<version>6.0.1</version>
</dependency>
spark-nlp-gpu:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-gpu_2.12</artifactId>
<version>6.0.1</version>
</dependency>
spark-nlp-silicon:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-silicon_2.12</artifactId>
<version>6.0.1</version>
</dependency>
spark-nlp-aarch64:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12</artifactId>
<version>6.0.1</version>
</dependency>
FAT JARs
- CPU on Apache Spark 3.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-assembly-6.0.1.jar
- GPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-gpu-assembly-6.0.1.jar
- M1 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-silicon-assembly-6.0.1.jar
- AArch64 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-aarch64-assembly-6.0.1.jar
What's Changed
- [SPARKNLP-1164] Updating python 3.7 to 3.8 for jobs spark34 and spark33 by @danilojsl #14565
- [SPARKNLP-1177] Solving typo in Python for RoBertaForMultipleChoice by @danilojsl #14567
- Sparknlp 1115 Introducing SmolVLM by @prabod #14552
- Fixing typos in notebooks by @ahmedlone127 #14570
- SparkNLP 1121 Introducing PaliGemma by @prabod #14551
- SparkNLP 1124 Introducing Gemma 3 by @prabod #14556
- Sparknlp-1158 Adding Parameters Options to PDF Reader by @danilojsl #14562
Full Changelog: 6.0.0...6.0.1
Spark NLP 6.0.0: PDF Reader, Excel Reader, PowerPoint Reader, Vision Language Models, Native Multimodal in GGUF, and many more!
📢 Spark NLP 6.0.0: A New Era for Universal Ingestion and Multimodal LLM Processing at Scale
From raw documents to multimodal insights at enterprise scale
With Spark NLP 6.0.0, we are setting a new standard for building scalable, distributed AI pipelines. This release transforms Spark NLP from a pure NLP library into the de facto platform for distributed LLM ingestion and multimodal batch processing.
This release introduces native ingestion for enterprise file types including PDFs, Excel spreadsheets, PowerPoint decks, and raw text logs, with automatic structure extraction, semantic segmentation, and metadata preservation — all in scalable, zero-code Spark pipelines.
At the same time, Spark NLP now natively supports Vision-Language Models (VLMs), loading quantized multimodal models like LLAVA, Phi Vision, DeepSeek Janus, and Llama 3.2 Vision directly via Llama.cpp, ONNX, and OpenVINO runtimes with no external inference servers, no API bottlenecks.
With 6.0.0, Spark NLP offers a complete, distributed architecture for universal data ingestion, multimodal understanding, and LLM batch inference at scale — enabling retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), document understanding, compliance audits, enterprise search, and multimodal analytics — all within the native Spark ecosystem.
One unified framework. Text, vision, documents — at Spark scale. Zero boilerplate. Maximum performance.
🌟 Spotlight Feature: AutoGGUFVisionModel — Native Multimodal Inference with Llama.cpp
Spark NLP 6.0.0 introduces the new AutoGGUFVisionModel, enabling native multimodal inference for quantized GGUF models directly within Spark pipelines. Powered by Llama.cpp, this annotator makes it effortless to run Vision-Language Models (VLMs) like LLAVA-1.5-7B Q4_0, Qwen2 VL, and others fully on-premises, at scale, with no external servers or APIs required.
With Spark NLP 6.0.0, Llama.cpp vision models are now first-class citizens inside DataFrames, delivering multimodal inference at scale with native Spark performance.
Why it matters
For the first time, Spark NLP supports pure vision-text workflows, allowing you to pass raw images and captions directly into LLMs that can describe, summarize, or reason over visual inputs.
This unlocks batch multimodal processing across massive datasets with Spark’s native scalability — perfect for product catalogs, compliance audits, document analysis, and more.
How it works
- Accepts raw image bytes (not Spark's OpenCV format) for true end-to-end multimodal inference.
- Provides a convenient helper function
ImageAssembler.loadImagesAsBytesto prepare image datasets effortlessly. - Supports all Llama.cpp runtime parameters like context length (
nCtx), top-k/top-p sampling, temperature, and repeat penalties, allowing fine control over completions.
Example usage
documentAssembler = DocumentAssembler() \
.setInputCol("caption") \
.setOutputCol("caption_document")
imageAssembler = ImageAssembler() \
.setInputCol("image") \
.setOutputCol("image_assembler")
data = ImageAssembler \
.loadImagesAsBytes(spark, "src/test/resources/image/") \
.withColumn("caption", lit("Caption this image."))
model = AutoGGUFVisionModel.pretrained() \
.setInputCols(["caption_document", "image_assembler"]) \
.setOutputCol("completions") \
.setBatchSize(4) \
.setNPredict(40) \
.setTopK(40) \
.setTopP(0.95) \
.setTemperature(0.05)
pipeline = Pipeline().setStages([documentAssembler, imageAssembler, model])
results = pipeline.fit(data).transform(data)
results.selectExpr("reverse(split(image.origin, '/'))[0] as image_name", "completions.result").show(truncate=False)📚 A full notebook walkthrough is available here.
🔥 New Features & Enhancements
PDF Reader
Font-aware PDF ingestion is now available with automatic page segmentation, encrypted file support, and token-level coordinate extraction, ideal for legal discovery and document Q&A.
Excel Reader
Spark NLP can now ingest .xls and .xlsx files directly into Spark DataFrames with automatic schema detection, multiple sheet support, and rich-text extraction for LLM pipelines.
PowerPoint Reader
Spark NLP introduces a native reader for .ppt and .pptx files. Capture slides, speaker notes, themes, and alt text at the document level for downstream summarization and retrieval.
Extractor and Cleaner Annotators
New Extractor and Cleaner annotators allow you to pull structured data (emails, IP addresses, dates) from text or clean noisy text artifacts like bullets, dashes, and non-ASCII characters at scale.
Text Reader
A high-performance TextReader is now available to load .txt, .csv, .log and similar files. It automatically detects encoding and line endings for massive ingestion jobs.
AutoGGUFVisionModel for Multimodal Llama.cpp Inference
Spark NLP now supports vision-language models in GGUF format using the new AutoGGUFVisionModel annotator. Run models like LLAVA-1.5-7B Q4_0 or Qwen2 VL entirely within Spark using Llama.cpp, enabling native multimodal batch inference without servers.
DeepSeek Janus Multimodal Model
The DeepSeek Janus model, tuned for instruction-following across text and images, is now fully integrated and available via a simple pretrained call.
Qwen-2 Vision-Language Model Catalog
Support for Alibaba’s Qwen-2 VL series (0.5B to 7B parameters) is now available. Use Qwen-2 checkpoints for OCR, product search, and multimodal retrieval tasks with unified APIs.
Native Multimodal Support with Phi-3.5 Vision
The new Phi3Vision annotator brings Microsoft’s Phi-3.5 multimodal model into Spark NLP. Process images and prompts together to generate grounded captions or visual Q&A results, all with a model footprint of less than 1 GB.
LLAVA 1.5 Vision-Language Transformer
Spark NLP now supports LLAVA 1.5 (7B) natively for screenshot Q&A, chart reading, and UI testing tasks. Build fully distributed multimodal inference pipelines without external services or dependencies.
Native Cohere Command-R Models
Cohere’s multilingual Command-R models (up to 35B parameters) are now fully integrated. Perform reasoning, RAG, and summarization tasks with no REST API latency and no token limits.
OLMo Family Support
Spark NLP now supports the full OLMo suite of open-weight language models (7B, 1.7B, and more) directly in Scala and Python. OLMo models come with full training transparency, Dolma-sized vocabularies, and reproducible experiment logs, making them ideal for academic research and benchmarking.
Multiple-Choice Heads for LLMs
New lightweight multiple-choice heads are now available for ALBERT, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, and XLM-RoBERTa models. These are perfect for building auto-grading systems, educational quizzes, and choice ranking pipelines.
AlbertForMultipleChoiceDistilBertForMultipleChoiceRoBertaForMultipleChoiceXlmRoBertaForMultipleChoice
VisionEncoderDecoder Improvements
The Scala API for VisionEncoderDecoder has been fully refactored to expose .generate() parameters like batch size and maximum tokens, aligning it one-to-one with the Python API.
🐛 Bug Fixes
Better GGUF Error Reporting
When a GGUF file is missing tensors or uses unsupported quantization, Spark NLP now provides clear and actionable error messages, including guidance on how to fix or convert the model.
Fixed MXBAI Typo
A small typo related to the MXBAI integration was corrected to ensure consistency across annotator names and pretrained model references.
VisionEncoderDecoder Alignment
The Scala VisionEncoderDecoder wrapper has been updated to fully match the Python API. It now exposes parameters like batch size and maximum tokens, fixing discrepancies that could occur in cross-language pipelines.
Minor Naming Improvements
Variable naming inconsistencies have been cleaned up throughout the codebase to ensure a more uniform and predictable developer experience.
📝 Models
We have added more than 110,000 new models and pipelines. The complete list of all 88,000+ models & pipelines in 230+ languages is available on our Models Hub.
❤️ Community support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas,
and show off how you use Spark NLP! - Medium Spark NLP articles
- JohnSnowLabs official Medium
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==6.0.0Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:6.0.0
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_...Spark NLP 5.5.3: Enhanced Embeddings, Fixed Attention Masks, Performance Optimizations, and 100K Free Models
📢 Spark NLP: Enhanced Embeddings, Fixed Attention Masks, and Performance Optimizations
Introduction
We’re excited to introduce the latest release of Spark NLP 5.5.3, featuring critical enhancements and bug fixes for several of our Text Embeddings annotators. These improvements ensure even more reliable and efficient performance for your NLP workflows.
But that’s not all—we’re also celebrating a major milestone: crossing 100,000 truly free and open models on our Models Hub! This achievement underscores our commitment to making state-of-the-art NLP accessible to everyone, forever.
Upgrade today to take advantage of these enhancements, and thank you for being part of the Spark NLP community. Your support and contributions continue to drive innovation forward!
🔥 Highlights
- Enhanced BGE Embeddings with configurable pooling strategies
- Fixed attention mask padding across multiple embedding models
- Major performance optimizations for transformer models
- Improved model default configurations and traits
🚀 New Features
Enhanced BGE Embeddings
Previously, BGE embeddings used a fixed pooling strategy that didn't match all model variants, resulting in suboptimal performance for some models (cosine similarity around 0.97 compared to the original implementation). Different BGE models are trained with different pooling strategies - some use CLS token pooling while others use attention-based average pooling.
- Added new
useCLSTokenparameter to control embedding pooling strategy - Changed default pretrained model from "bge_base" to "bge_small_en_v1.5"
val embeddings = BGEEmbeddings.pretrained("bge_small_en_v1.5")
.setUseCLSToken(true) // Use CLS token pooling (default)
.setInputCols("document")
.setOutputCol("embeddings")🛠 Improvements & Bug Fixes
Attention Mask Fixes
Fixed incorrect padding in attention mask calculations for multiple models:
- MPNet
- BGE
- E5
- Mxbai
- Nomic
- SnowFlake
- UAE
This fix ensures consistent results between native implementations and ONNX versions.
Other Fixes
- Fixed Llama3 download issues in Python
- Optimized OpenVINO and ONNX inference paths
- Enhanced code cleanup and standardization
🔄 Breaking Changes
BGE Embeddings Updates
-
Default Model Change:
- Old default: "bge_base"
- New default: "bge_small_en_v1.5"
- Action required: Explicitly specify "bge_base" if needed
-
Pooling Strategy:
- New
useCLSTokenparameter defaults to True - May affect embedding calculations
- Action required: Verify existing implementations and set parameter explicitly if needed
- New
💡 Usage Examples
Specifying BGE Model Version
// Using new default
val embeddingsNew = BGEEmbeddings.pretrained()
// Using previous default explicitly
val embeddingsOld = BGEEmbeddings.pretrained("bge_base")Configuring Pooling Strategy
// Using CLS token pooling
val embeddingsCLS = BGEEmbeddings.pretrained()
.setUseCLSToken(true)
// Using attention-based average pooling
val embeddingsAvg = BGEEmbeddings.pretrained()
.setUseCLSToken(false)❤️ Community support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas,
and show off how you use Spark NLP! - Medium Spark NLP articles
- JohnSnowLabs official Medium
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==5.5.3Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.5.3
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.5.3GPU
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.5.3
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.5.3Apple Silicon (M1 & M2)
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.5.3
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.5.3AArch64
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.5.3
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.5.3Maven
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.3</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-gpu:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-gpu_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.3</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-silicon:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-silicon_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.3</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-aarch64:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.3</version>
</dependency>FAT JARs
-
CPU on Apache Spark 3.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-assembly-5.5.3.jar
-
GPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-gpu-assembly-5.5.3.jar
-
M1 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-silicon-assembly-5.5.3.jar
-
AArch64 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-aarch64-assembly-5.5.3.jar
What's Changed
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14490
- LLama3 download fix by @C-K-Loan in #14508
- Bugfix: wrong attention mask calculation resulted in wrong embeddings by @maziyarpanahi in #14496
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14513
- Release/553 release candidate by @maziyarpanahi in #14511
Full Changelog: 5.5.2...5.5.3
Spark NLP 5.5.2: GGUF Embeddings, New HTML/Email/Word Ingestion, Enhanced OpenVINO Support, a New Q&A Annotator, and More Enhancements & Fixes
📢 Spark NLP 5.5.2
We’re thrilled to introduce the latest enhancements and new features in this release of Spark NLP! These additions bring more powerful model inference capabilities, seamless data ingestion methods, and greater flexibility for scaling your NLP workflows.
Upgrade today to take advantage of these new capabilities and improvements. As always, we look forward to your feedback and contributions, and thank you for being part of the Spark NLP community!
🔥 New Features & Enhancements
🚀 Major New Features
-
OpenVINO Support for Transformers (#14408)
Many popular transformer-based annotators now leverage OpenVINO for faster inference on Intel hardware. Enjoy speedier pipelines across a wide array of models—such as DeBerta, DistilBert, RoBerta, XlmRoBerta, Albert, and more—enabling efficient, production-grade NLP at scale. -
BLIPForQuestionAnswering Transformer (#14422)
Introducing BLIPForQuestionAnswering, a new image-based question-answering transformer. Simply provide an image and a question, and BLIP will deliver contextually relevant answers. Perfect for use cases in image analysis, e-commerce, and beyond. -
AutoGGUFEmbeddings Annotator (#14433)
Seamlessly integrate AutoGGUFModels into your NLP pipeline. The new AutoGGUFEmbeddings annotator provides dense vector embeddings, making it easier than ever to incorporate advanced sentence embeddings into your workflows. We’ve included an end-to-end notebook to help you get started right away.
📜 New Data Ingestions
-
Parsing HTML to DataFrames (#14449)
Need to analyze web content at scale? Use sparknlp.read().html() to parse local or remote HTML files into structured Spark DataFrames. This new feature makes web-scale data analysis and downstream NLP tasks more accessible and scalable. -
Email Content to DataFrames (#14455)
Leveragesparknlp.read().email()to transform email content into organized DataFrames. Analyze communications, extract insights, and enrich your NLP pipelines with minimal effort. (Requires #14449 to be merged first.) -
Microsoft Word Document Parsing (#14476)
Turn .docx and .doc files into structured Spark DataFrames for streamlined integration into your NLP projects. From enterprise documents to reports, this feature simplifies data preparation and analysis at scale.
🐛 Bug Fixes
-
Microsoft Fabric Integration (#14467)
We’ve added support for Microsoft Fabric to store and retrieve word embeddings efficiently. Leverage your existing infrastructure to scale Spark NLP solutions more effectively. -
cuDNN Upgrade Instructions for Databricks (#14451)
Easily upgrade cuDNN on Databricks to accelerate ONNX model inference on GPU, and take advantage of updated installation instructions for a cleaner setup. -
Metadata Preservation in ChunkEmbeddings (#14462)
ChunkEmbeddings now retain original metadata, ensuring richer context and more meaningful insights in your downstream tasks. -
Default Names and Languages for New Annotators (#14469)
We’ve standardized default names and languages in our seq2seq annotators for better clarity, consistency, and ease of use.
📦 Dependencies
Updated:
- Jsoup has been updated from 1.18.1 to 1.18.2 to ensure compatibility and maintain security and performance standards.
New Additions for Email and Document Parsing:
-
Jakarta Mail (jakarta.mail:jakarta.mail-api:2.1.3): Added to support parsing and processing email content.
-
Angus Mail (org.eclipse.angus:angus-mail:2.0.3): Complementary mail handling library integrated for more robust email parsing capabilities.
-
Apache POI (org.apache.poi:poi-ooxml:4.1.2 & org.apache.poi:poi-scratchpad:4.1.2): Introduced for parsing Word documents (.docx and .doc) into structured DataFrames, enabling seamless integration of document-based data into Spark NLP workflows.
❤️ Community support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas,
and show off how you use Spark NLP! - Medium Spark NLP articles
- JohnSnowLabs official Medium
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==5.5.2Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.5.2
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.5.2GPU
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.5.2
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.5.2Apple Silicon (M1 & M2)
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.5.2
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.5.2AArch64
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.5.2
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.5.2Maven
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.2</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-gpu:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-gpu_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.2</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-silicon:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-silicon_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.2</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-aarch64:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.2</version>
</dependency>FAT JARs
-
CPU on Apache Spark 3.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-assembly-5.5.2.jar
-
GPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-gpu-assembly-5.5.2.jar
-
M1 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-silicon-assembly-5.5.2.jar
-
AArch64 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-aarch64-assembly-5.5.2.jar
What's Changed
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14458
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14470
- adding openvino support to all ClassificationForXXX annotators by @ahmedlone127 in #14408
- [SPARKNLP-1068] Introducing BLIPForQuestionAnswering transformer by @danilojsl in #14422
- [SPARKNLP-1091] AutoGGUFModel embeddings support by @DevinTDHa in #14433
- Apache Spark vulnerable Fix by @maziyarpanahi in #14441
- [SPARKNLP-1092] Adding support to read HTML files by @danilojsl in #14449
- [SPARKNLP-1095] Add installation instructions for ONNX GPU on Databricks by @DevinTDHa in #14451
- [SPARKNLP-1093] Adding support to read Email files by @danilojsl in #14455
- Small typos by @svlandeg in #14459
- Addition chunk metadata to ChunkEmbeddings output by @mehmetbutgul in #14462
- [SPARKNLP-1096] Adding support to Microsoft Fabric for WordEmbeddings by @danilojsl in #14467
- Default name updates by @ahmedlone127 in #14469
- SPARKNLP-1094 Adding Support to Read Word Files by @danilojsl in #14476
- ignore html as linguist-vendored by @maziyarpanahi in #14481
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14482
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14485
- Spark NLP 5.5.2 Release Candidate by @maziyarpanahi in #14473
New Contributors
Full Changelog: 5.5.1...5.5.2
Spark NLP 5.5.1: Patch release
🔥 Enhancements & Bug Fixes
BertForMultipleChoiceTransformer Added. Enhanced BERT’s capabilities to handle multiple-choice tasks such as standardized test questions and survey or quiz automation.PromptAssemblerAnnotator Introduced. Introduced a new annotator that constructs prompts for LLMs using a chat template and a sequence of messages. Accepts an array of tuples with roles (“system”, “user”, “assistant”) and message texts. Utilizes llama.cpp as a backend for template parsing, supporting basic template applications.
Example Notebook
promptAssembler = (
PromptAssembler()
.setInputCol("messages")
.setOutputCol("prompt")
.setChatTemplate(template)
)- Integrated New Tasks and Documentation. Added support and documentation for the following tasks:
- Automatic Speech Recognition
- Dependency Parsing
- Image Captioning
- Image Classification
- Landing Page
- Question Answering
- Summarization
- Table Question Answering
- Text Classification
- Text Generation
- Text Preprocessing
- Token Classification
- Translation
- Zero-Shot Classification
- Zero-Shot Image Classification
- Resolved Pretrained Model Loading Issue on
DBFS Systems. - Fixed a bug where pretrained models were not found when running
AutoGGUFModelpipelines onDatabricksdue to incorrect path handling of gguf files.
📖 Documentation
- Import models from TF Hub & HuggingFace
- Spark NLP Notebooks
- Models Hub with new models
- Spark NLP Articles
- Spark NLP in Action
- Spark NLP Documentation
- Spark NLP Scala APIs
- Spark NLP Python APIs
❤️ Community support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas, and show off how you use Spark NLP!
- Medium Spark NLP articles
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==5.5.1Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x: (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.5.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.5.1GPU
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.5.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.5.1Apple Silicon (M1 & M2)
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.5.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.5.1AArch64
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.5.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.5.1Maven
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.1</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-gpu:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-gpu_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.1</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-silicon:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-silicon_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.1</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-aarch64:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.1</version>
</dependency>FAT JARs
-
CPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-assembly-5.5.1.jar
-
GPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-gpu-assembly-5.5.1.jar
-
M1 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-silicon-assembly-5.5.1.jar
-
AArch64 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-aarch64-assembly-5.5.1.jar
What's Changed
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14418
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14420
- Add a new llama_cpp engine by @maziyarpanahi in #14436
- tasks-docs-integration by @AbdullahMubeenAnwar in #14428
- Introducing BertForMultipleChoice transformer by @danilojsl in #14435
- Fix pretrained models not being found on dbfs systems by @DevinTDHa in #14438
- [SPARKNLP-1067] PromptAssembler by @DevinTDHa in #14439
- Release/551 release candidate by @maziyarpanahi in #14437
Full Changelog: 5.5.0...5.5.1
Spark NLP 5.5.0: Launching Llama.cpp Integration, Llama3, QWEN2, Phi-3, StarCoder2, MiniCPM, NLLB, Nomic, Snowflake, MxBai, more ONNX and OpenVino integrations, more than 50,000 new models, and many more!
📢 Spark NLP 5.5.0: Unlocking New Horizons with Llama.cpp Integration and More!
We're thrilled to announce the release of Spark NLP 5.5.0, a groundbreaking update that pushes the boundaries of natural language processing! This release is packed with exciting new features, optimizations, and integrations that will transform your NLP workflows. At the heart of this update is our game-changing integration with Llama.cpp, but that's just the beginning of what's in store!
🌟 Spotlight Feature: Llama.cpp Integration
Introducing Llama.cpp Integration: A New Era of Efficient Language Models!
We're proud to present the centerpiece of Spark NLP 5.5.0: the integration of Llama.cpp! This revolutionary addition brings unparalleled efficiency and performance to large language models within the Spark NLP ecosystem.
- Optimized Performance: Llama.cpp's C/C++ implementation allows for blazing-fast inference on CPUs, making large language models more accessible than ever.
- Reduced Memory Footprint: Enjoy the power of advanced language models with significantly lower RAM requirements.
- Quantization Support: Take advantage of various quantization options to further optimize model size and speed without sacrificing quality.
- Seamless Integration: Easily incorporate Llama.cpp models into your existing Spark NLP pipelines with our new
AutoGGUFModelannotator.
This integration opens up new possibilities for deploying state-of-the-art language models in resource-constrained environments, making advanced NLP capabilities available to a wider range of applications and users.
We extend our heartfelt thanks to all contributors who made this release possible. Your innovative ideas, code contributions, and feedback continue to drive Spark NLP forward. Our Models Hub now contains over 83,000+ free and truly open-source models & pipelines. 🎉
🔥 New Features & Enhancements
Introducing QWEN2Transformer
We have added the QWEN2Transformer annotator, supporting the Qwen-2 model architecture known for its efficiency and performance in various NLP tasks like text generation and summarization.
Introducing MiniCPM
The MiniCPM annotator is now available, providing support for the MiniCPM model designed for efficient language modeling with smaller parameter sizes without compromising performance.
Introducing NLLB (No Language Left Behind)
We are excited to include the NLLB annotator, supporting No Language Left Behind models aimed at providing high-quality machine translation capabilities for a wide range of languages, especially low-resource languages.
Implementing Nomic Embeddings
Introducing support for Nomic Embeddings, which provide robust semantic representations for downstream tasks like clustering and classification.
Snowflake Integration
We have implemented integration with Snowflake, allowing seamless data transfer and processing between Spark NLP and Snowflake data warehouses.
Introducing CamemBertForZeroShotClassification
The CamemBertForZeroShotClassification annotator is now available, enabling zero-shot classification capabilities using the CamemBERT model, optimized for French language processing.
Implementing MxBai Embeddings
We have added support for MxBaiEmbeddings, providing embeddings from the MxBai model designed for multilingual text representation.
ONNX Support for Vision Annotators
We have extended ONNX support to our vision annotators, allowing for optimized and accelerated inference for image-related NLP tasks.
OpenVINO and ONNX Support for Additional Annotators
Building upon our commitment to performance optimization, we have added OpenVINO and ONNX support to several additional annotators, ensuring you can leverage hardware acceleration across a broader range of models.
Introducing AlbertForZeroShotClassification
We are excited to introduce the AlbertForZeroShotClassification annotator, bringing zero-shot classification capabilities using the ALBERT model known for its parameter efficiency and strong performance.
Introducing Phi-3
We have integrated Phi-3 models into Spark NLP, providing enhanced performance with high-efficiency quantization, supporting INT4 and INT8 quantization for CPUs via OpenVINO.
Introducing StarCoder2 for Causal Language Modeling
The StarCoder2 model is now supported for causal language modeling tasks, enabling advanced code generation and understanding capabilities.
Introducing LLAMA 3
Continuing our support for the latest in language modeling, we have introduced support for LLAMA 3, bringing the latest advancements in the LLaMA model series to Spark NLP.
🐛 Bug Fixes
- OpenVINO Installation Instructions: Updated the installation instructions for OpenVINO to ensure a smoother setup process.
- Fixed Default Auto GGUF Pretrained Model: Addressed issues with the default auto GGUF pretrained model in the Llama.cpp integration.
View Pull Requests, View Pull Request
- Updated Models Hub: Improved the Models Hub for better accessibility and search functionality.
View Pull Requests, View Pull Request, View Pull Request
- Artifact Creation Optimization: Switched to using 7zip instead of
vimtor/action-zipfor creating artifacts to enhance compatibility and performance.
📦 Dependencies
-
Published New OpenVINO Artifacts: Built and published new OpenVINO artifacts for both CPU and GPU to enhance performance and compatibility.
-
Upgraded ONNX Runtime: Updated
onnxruntimeto the latest version for improved stability and performance on both CPU and GPU.
📝 Models
We have added more than 50,000 new models and pipelines. The complete list of all 83,000+ models & pipelines in 230+ languages is available on our Models Hub.
❤️ Community support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas,
and show off how you use Spark NLP! - Medium Spark NLP articles
- JohnSnowLabs official Medium
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==5.5.0Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.5.0
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.5.0GPU
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.5.0
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.5.0Apple Silicon (M1 & M2)
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.5.0
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.5.0AArch64
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.5.0
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.5.0Maven
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.0</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-gpu:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-gpu_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.5.0</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-silicon:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-silicon...Spark NLP 5.4.2: Patch release
🔥 Enhancements & Bug Fixes
- Added demo notebook for Image Classification Annotators #14360
- Added
aggressiveMatchingparameter toDateMatcherandMultiDateMatcherannotators #14365 - Added
aggressiveMatchingparameter toDocumentSimilarityRankerannotator #14370
📖 Documentation
- Import models from TF Hub & HuggingFace
- Spark NLP Notebooks
- Models Hub with new models
- Spark NLP Articles
- Spark NLP in Action
- Spark NLP Documentation
- Spark NLP Scala APIs
- Spark NLP Python APIs
❤️ Community support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas, and show off how you use Spark NLP!
- Medium Spark NLP articles
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==5.4.2Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x: (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.4.2
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.4.2GPU
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.4.2
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.4.2Apple Silicon (M1 & M2)
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.4.2
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.4.2AArch64
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.4.2
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.4.2Maven
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.4.2</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-gpu:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-gpu_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.4.2</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-silicon:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-silicon_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.4.2</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-aarch64:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.4.2</version>
</dependency>FAT JARs
-
CPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-assembly-5.4.2.jar
-
GPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-gpu-assembly-5.4.2.jar
-
M1 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-silicon-assembly-5.4.2.jar
-
AArch64 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-aarch64-assembly-5.4.2.jar
What's Changed
- fixies in docs by @agsfer in #14357
- release/542-release-candidate by @maziyarpanahi in #14381
Full Changelog: 5.4.1...5.4.2
Spark NLP 5.4.1: Patch release
🔥 New Features & Enhancements
- Added support for loading duplicate models in Spark NLP, allowing multiple models from the same annotator to be loaded simultaneously.
- Updated the README for better coherence and added new pages to the website.
- Added support for a stop IDs list to halt text generation in Phi, Mistral, and Llama annotators.
🐛 Bug Fixes
- Fixed the default model names for Phi2 and Mistral AI annotators.
📖 Documentation
- Import models from TF Hub & HuggingFace
- Spark NLP Notebooks
- Models Hub with new models
- Spark NLP Articles
- Spark NLP in Action
- Spark NLP Documentation
- Spark NLP Scala APIs
- Spark NLP Python APIs
❤️ Community support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas, and show off how you use Spark NLP!
- Medium Spark NLP articles
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==5.4.1Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x: (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.4.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.4.1GPU
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.4.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.4.1Apple Silicon (M1 & M2)
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.4.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.4.1AArch64
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.4.1
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.4.1Maven
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.4.1</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-gpu:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-gpu_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.4.1</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-silicon:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-silicon_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.4.1</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-aarch64:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.4.1</version>
</dependency>FAT JARs
-
CPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-assembly-5.4.1.jar
-
GPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-gpu-assembly-5.4.1.jar
-
M1 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-silicon-assembly-5.4.1.jar
-
AArch64 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-aarch64-assembly-5.4.1.jar
What's Changed
- Fixing default names for Phi2 and MistralAI by @ahmedlone127 in #14338
- [SPARKNLP-1052] Adding random suffix to avoid duplication in spark files by @danilojsl in #14340
- [SPARKNLP-1015] Restructuring Readme and Documentation by @danilojsl in #14341
- Added custom stop token id support by @prabod in #14344
- Update 2023-03-01-t5_flan_base_xx.md by @dcecchini in #14345
- Spark NLP 5.4.1 by @maziyarpanahi in #14350
Full Changelog: 5.4.0...5.4.1
Spark NLP 5.4.0: Launching OpenVINO Runtime Integration, Advanced Model Support for LLMs, Enhanced Performance with New Annotators, Improved Cloud Scalability, and Comprehensive Updates Across the Board!
📢 It's All About LLMs!
We're excited to share some amazing updates in the latest Spark NLP release of Spark NLP 🚀 5.4.0! This update is packed with new features and improvements that are set to transform natural language processing. One of the highlights is the integration of OpenVINO Runtime, which significantly boosts performance and efficiency across Intel hardware. You can now enjoy up to a 40% increase in performance compared to TensorFlow, with support for various model formats like ONNX, PaddlePaddle, TensorFlow, and TensorFlow Lite.
We've also added some powerful new annotators: BertEmbeddings, RoBertaEmbeddings, and XlmRoBertaEmbeddings. These are specially fine-tuned to take full advantage of the OpenVINO toolkit, offering better model accuracy and speed.
Another big change is in how we distribute models. We've moved from Broadcast to addFile for model distribution, which makes it easier to scale and manage large language models (LLMs) in cloud environments. This is especially helpful for models with over 7 billion parameters.
In addition, we've introduced the Mistral and Phi-2 architectures, optimized for high-efficiency quantization. There are also practical improvements to core components, like enhanced pooling for BERT-based models and updates to the OpenAIEmbeddings annotator for better performance and integration.
We want to thank our community for their valuable feedback, feature requests, and contributions. Our Models Hub now contains over 37,000+ free and truly open-source models & pipelines. 🎉
Spark NLP ❤️ OpenVINO
🔥 New Features & Enhancements
NEW Integration: OpenVINO Runtime for Spark NLP 🚀: We're thrilled to announce the integration of OpenVINO Runtime, enhancing Spark NLP with high-performance inference capabilities. OpenVINO Runtime supports direct reading of models in ONNX, PaddlePaddle, TensorFlow, and TensorFlow Lite formats, enabling out-of-the-box optimizations and superior performance on supported Intel hardware.
Enhanced Model Support and Performance Gains: The integration allows Spark NLP to utilize the OpenVINO Runtime API for Java, facilitating the loading and execution of models across various formats including ONNX, PaddlePaddle, TensorFlow, TensorFlow Lite, and OpenVINO IR. Impressively, benchmarks show up to a 40% performance improvement over TensorFlow with no additional tuning required. Additionally, users can harness the full optimization and quantization capabilities of the OpenVINO toolkit via the Model Conversion API.
Enabled Annotators: This update brings OpenVINO compatibility to a range of Spark NLP annotators, including BertEmbeddings, RoBertaEmbeddings, XlmRoBertaEmbeddings, T5Transformer, E5Embeddings, LLAMA2, Mistral, Phi2, and M2M100.
Acknowledgements: This significant enhancement was accomplished during Google Summer of Code 2023. Special thanks to Rajat Krishna (@rajatkrishna) and the entire OpenVINO team for their invaluable support and collaboration. #14200


- New Mistral Integration: We are excited to introduce the
Mistralintegration, featuring models fine-tuned on theMistralForCasualLMarchitecture. This addition enhances performance and efficiency by supporting quantization in INT4 and INT8 for CPUs via OpenVINO. #14318
 > Performance of Mistral 7B and different Llama models on a wide range of benchmarks. For all metrics, all models were re-evaluated with our evaluation pipeline for accurate comparison. Mistral 7B significantly outperforms Llama 2 13B on all metrics, and is on par with Llama 34B (since Llama 2 34B was not released, we report results on Llama 34B). It is also vastly superior in code and reasoning benchmarks. https://mistral.ai/news/announcing-mistral-7b/
> Performance of Mistral 7B and different Llama models on a wide range of benchmarks. For all metrics, all models were re-evaluated with our evaluation pipeline for accurate comparison. Mistral 7B significantly outperforms Llama 2 13B on all metrics, and is on par with Llama 34B (since Llama 2 34B was not released, we report results on Llama 34B). It is also vastly superior in code and reasoning benchmarks. https://mistral.ai/news/announcing-mistral-7b/
Continuing our commitment to user-friendly and scalable solutions, the integration of the Mistral architecture has been designed to be straightforward and easily adoptable, ensuring that users can leverage these enhancements without complexity:
doc_assembler = DocumentAssembler() \
.setInputCol("text") \
.setOutputCol("document")
mistral = MistralTransformer \
.pretrained() \
.setMaxOutputLength(50) \
.setDoSample(False) \
.setInputCols(["document"]) \
.setOutputCol("mistral_generation")- New Phi-2 Integrations: Introducing
Phi-2, featuring models fine-tuned using thePhiForCausalLMarchitecture. This update enhances OpenVINO's capabilities, enabling quantization in INT4 and INT8 for CPUs to optimize both performance and efficiency. #14318
Continuing our commitment to user-friendly and scalable solutions, the integration of the Phi architecture has been designed to be straightforward and easily adoptable, ensuring that users can leverage these enhancements without complexity:
doc_assembler = DocumentAssembler() \
.setInputCol("text") \
.setOutputCol("document")
phi2 = Phi2Transformer \
.pretrained() \
.setMaxOutputLength(50) \
.setDoSample(False) \
.setInputCols(["document"]) \
.setOutputCol("phi2_generation")- NEW: Enhanced LLM Distribution: We've optimized the scalability of large language models (LLMs) in the cloud by transitioning from Broadcast to
addFilefor deep learning distribution across any cluster. This change addresses the challenges of handling modern LLMs—some boasting over 7 billion parameters—by improving memory management and overcoming serialization limits previously encountered with Java Bytes and Apache Spark's Broadcast method. This update significantly boosts Spark NLP's ability to process LLMs efficiently, underscoring our dedication to delivering scalable NLP solutions.#14236
-
NEW: MPNetForTokenClassification Annotator: Introducing the
MPNetForTokenClassificationannotator in Spark NLP 🚀. This annotator efficiently loads MPNet models equipped with a token classification head (a linear layer atop the hidden-states output), ideal for Named-Entity Recognition (NER) tasks. It supports models trained or fine-tuned in ONNX format usingMPNetForTokenClassificationfor PyTorch orTFCamembertForTokenClassificationfor TensorFlow from HuggingFace 🤗. [View Pull Request](#14322 -
Enhanced Pooling for BERT, RoBERTa, and XLM-RoBERTa: We've added support for average pooling in
BertSentenceEmbeddings,RoBertaSentenceEmbeddings, andXLMRoBertaEmbeddingsannotators. This feature is especially useful when the [CLS] token is not fine-tuned for sentence embeddings via average pooling. View Pull Request -
Refined OpenAIEmbeddings: Upgraded to support escape characters to prevent JSON content issues, changed the output annotator type from
DOCUMENTtoSENTENCE_EMBEDDINGS(note: this affects backward compatibility), enhanced output embeddings with metadata from the document column, introduced a Python unit test class, and added a new submodule for reliable saving/loading of the annotator. View Pull Request -
New OpenVINO Notebooks: Released notebooks for exporting HuggingFace models using Optimum Intel and importing into Spark NLP. This update includes notebooks for
BertEmbeddings,E5Embeddings,LLAMA2Transformer,RoBertaEmbeddings,XlmRoBertaEmbeddings, andT5Transformer. View Pull Request
🐛 Bug Fixes
- Resolved Connection Timeout Issue: Fixed the
Timeout waiting for connection from poolerror that occurred when downloading multiple models simultaneously. View Pull Request - Corrected Llama-2 Decoder Position ID: Addressed an issue where the Llama-2 decoder received an incorrect next position ID. View Pull Request
- Stabilized BertForZeroShotClassification: Fixed crashes in sentence-wise pipelines by implementing a method to pad all required arrays within a batch to the same length. View Pull Request
- Updated Transformers Dependency: Resolved the import issue with
keras.engineby updating the transformers version to4.34.1. View Pull Request - ONNX Model Version Compatibility: Fixed
Unsupported model IR version: 10, max supported IR version: 9by setting the ONNX version toonnx==1.14.0. View Pull Request - Resolved Breeze Compatibility Issue: Addressed
java.lang.NoSuchMethodErrorby ensuring compatibility with Spark 3.4 and updating documentation accordingly. [View Pull Request](https://github.com/Jo...
Spark NLP 5.3.3: Patch release
🔥 New Features & Enhancements
- NEW: Introducing
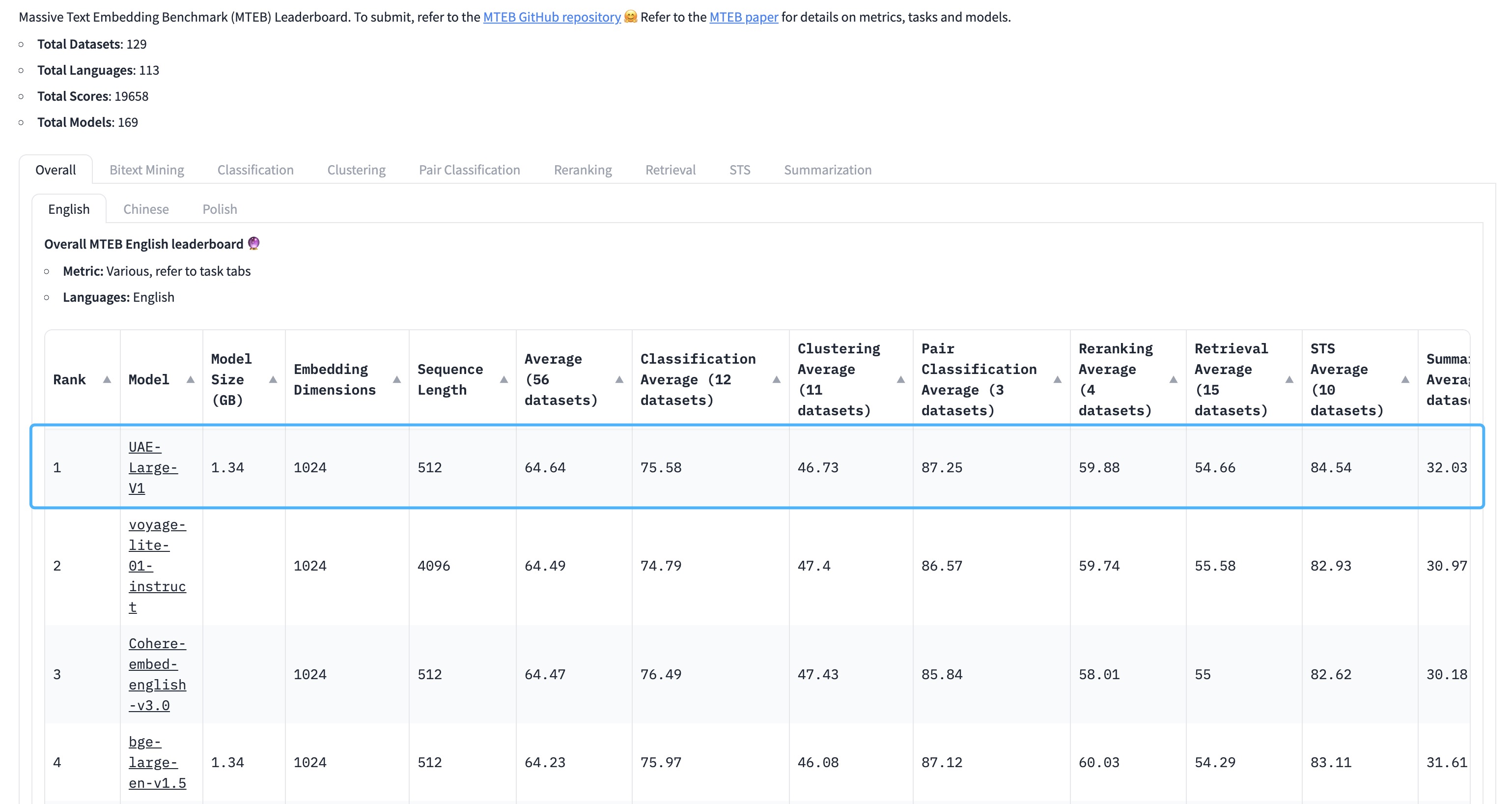
UAEEmbeddingsfor sentence embeddings using Universal AnglE Embedding, aimed at improving semantic textual similarity tasks.
UAE is a novel angle-optimized text embedding model, designed to improve semantic textual similarity tasks, which are crucial for Large Language Model (LLM) applications. By introducing angle optimization in a complex space, AnglE effectively mitigates saturation of the cosine similarity function. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.12871.pdf
🔥 The universal English sentence embedding WhereIsAI/UAE-Large-V1 achieves SOTA on the MTEB Leaderboard with an average score of 64.64!
- Introduce critical enhancements and optimizations to the processing of the CoNLL-U format for Dependency Parsers training, including enhanced multiword token handling and improved handling of missing uPos values
- Implement cache mechanism for
metadata.json, enhancing efficiency by avoiding unnecessary downloads - Add example notebook for
DocumentCharacterTextSplitter - Add example notebook for
DeBertaForZeroShotClassification - Add example notebooks for
BGEEmbeddingsandMPNetEmbeddings - Add example notebook for
MPNetForQuestionAnswering - Add example notebook for
MPNetForSequenceClassification
🐛 Bug Fixes
- Address a bug with serializing ONNX models that lack a
.onnx_datafile, ensuring better reliability in model serialization processes - Delete redundant
Multilingual_Translation_with_M2M100.ipynbnotebook entries - Fix Colab link for the M2M100 notebook
📖 Documentation
- Import models from TF Hub & HuggingFace
- Spark NLP Notebooks
- Models Hub with new models
- Spark NLP Articles
- Spark NLP in Action
- Spark NLP Documentation
- Spark NLP Scala APIs
- Spark NLP Python APIs
❤️ Community support
- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas, and show off how you use Spark NLP!
- Medium Spark NLP articles
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
Installation
Python
#PyPI
pip install spark-nlp==5.3.3Spark Packages
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x: (Scala 2.12):
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.3.3
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp_2.12:5.3.3GPU
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.3.3
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-gpu_2.12:5.3.3Apple Silicon (M1 & M2)
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.3.3
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-silicon_2.12:5.3.3AArch64
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.3.3
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.nlp:spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12:5.3.3Maven
spark-nlp on Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.3.3</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-gpu:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-gpu_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.3.3</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-silicon:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-silicon_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.3.3</version>
</dependency>spark-nlp-aarch64:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.johnsnowlabs.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-nlp-aarch64_2.12</artifactId>
<version>5.3.3</version>
</dependency>FAT JARs
-
CPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-assembly-5.3.3.jar
-
GPU on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-gpu-assembly-5.3.3.jar
-
M1 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-silicon-assembly-5.3.3.jar
-
AArch64 on Apache Spark 3.0.x/3.1.x/3.2.x/3.3.x/3.4.x/3.5.x: https://s3.amazonaws.com/auxdata.johnsnowlabs.com/public/jars/spark-nlp-aarch64-assembly-5.3.3.jar
What's Changed
- Uploading missing notebooks from Spark NLP v 5.1.4 by @AbdullahMubeenAnwar in #14196
- SPARKNLP-962: UAEEmbeddings by @DevinTDHa in #14199
- Cache mechanism implementation for metadata.json by @mehmetbutgul in #14224
- [SPARKNLP-1031] Solves Dependency Parsers training issue by @danilojsl in #14225
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14228
- release/533-release-candidate by @maziyarpanahi in #14227
- Models hub by @maziyarpanahi in #14230
Full Changelog: 5.3.2...5.3.3