SelfElicit is an inference-time context augmentation framework for context-based Question Answering (QA). It leverages the inherent ability of specific attention layers of pre-trained language models (LMs) to automatically extract and highlight key evidence from the context passage, helping the LM focus on critical information and providing more accurate and factually grounded answers. The approach is model-agnostic, computationally efficient, and does not require additional training.

Overview of SelfElicit Workflow.
Please see run_experiment.ipynb for a step-by-step guide for running the experiments and visualizing results.
- 💡Automatic Evidence Highlighting: SelfElicit uses attention patterns in LMs to automatically identify crucial evidence within the context, thereby helping the model to focus on relevant information.
- 🚀Model-Agnostic Booster: Boost with various families of LMs with different sizes and architectures, tested with Llama3.1 (8B, 70B), Mistral (7B, 12B), and Qwen2.5 (7B, 32B).
- 🪽Light-weight Inference-Time Augmentation: Applies evidence selection and context highlighting during inference, without requiring iterative prompting or additional training.
Please cite us if you find our work or this repository helpful in your research : )
@article{liu2025selfelicit,
title={SelfElicit: Your Language Model Secretly Knows Where is the Relevant Evidence},
author={Liu, Zhining and Amjad, Rana Ali and Adkathimar, Ravinarayana and Wei, Tianxin and Tong, Hanghang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.08767},
year={2025}
}- 🌈 SelfElicit Features
- 🤗 Citing SelfElicit
- 📑 Table of Contents
- 🛫 Quick Start
- 📈 Results and Examples
- 🗂️ Code Structure
Please see the requirements.txt file for the required Python packages. You can install them using the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtWe provide an example Jupyter notebook run_experiment.ipynb to run experiments and visualize results.
Alternatively, you can run the experiment using the command-line interface with run_experiment.py.
Follow these steps to run an experiment:
-
Configure the Experiment:
Edit theconfig.yamlfile to set up your HuggingFace API token, model paths, datasets, and other parameters. -
Run the Experiment:
- Jupyter Notebook (Recommended):
- Open
run_experiment.ipynbin Jupyter. - Run the cells to load the data, set up the QA agents, and run the experiments.
- Visualize the results and compare different methods on various datasets.
- Open
- Command-line Interface:
An example command to run the experiment with the Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct model:You can configure the experiment by changing the passed arguments if you want to test something different than in thepython run_experiment.py --model_id "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct"config.yamlfile. Please see the desciption of arguments andargs.pyfor more details.
- Jupyter Notebook (Recommended):
-
Results:
The results will be saved in theresultsdirectory, containing the true answers, model's answers, and evaluation metric scores for each method and dataset.
| Argument | Description | Default (Valid Options) |
|---|---|---|
--hf_token |
Hugging Face API token. | "your_hf_api_token" (Replace with your own token) |
--model_id |
The HuggingFace Model ID. Should be one of the specified models. | "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" ("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct", "mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3", "mistralai/Mistral-Nemo-Instruct-2407", "Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct", "Qwen/Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct") |
--methods |
Method(s) to test. Can be a list or a single value. | ["Base", "COT", "FullElicit", "PromptElicit", "SelfElicit"] |
--datasets |
Dataset(s) to use. Can be a list or a single value. | ["HotpotQA", "NewsQA", "TQA", "NQ"] |
--alpha |
Threshold for the SelfElicit method. | 0.5 |
--layer_span |
A tuple representing the layer span for the SelfElicit method. | (0.5, 1.0) (Must be a tuple of two floats between [0, 1]) |
--gpu_ids |
List of GPU IDs to use for computation. | [0] (Auto-detected if not specified) |
--n_samples |
Number of samples in each dataset. | 1000 (Set to None to use the full data) |
--random_state |
The random state for reproducibility. | 0 |
--max_ans_tokens |
Maximum length of the answer in tokens. | 100 |
--marker_impstart |
Marker indicating the start of important information in the context. | "<START_IMPORTANT>" |
--marker_impend |
Marker indicating the end of important information in the context. | "<END_IMPORTANT>" |
--qa_inst |
Instruction for context-based QA. | "Directly answer the question based on the context passage, no explanation is needed. If the context does not contain any evidence, output 'I cannot answer based on the given context.'" |
--se_inst |
Instruction for context-based QA with SelfElicit highlighting. Must contain markers. | "Directly answer the question based on the context passage, no explanation is needed. Within the context, {MARKER_IMPSTART} and {MARKER_IMPEND} are used to mark the important evidence. Read carefully but still keep your answer short, do not output the markers. If the context does not contain any evidence, output 'I cannot answer based on the given context.'" |
--cot_inst |
Instruction for context-based QA with Chain-of-Thought (COT) prompting. | "Directly answer the question based on the context passage, no explanation is needed. If the context does not contain any evidence, output 'I cannot answer based on the given context.' Think step by step to provide the answer." |
--pe_inst |
Instruction for extracting evidence from the context (1st step of PromptElicit). | "Please find the supporting evidence sentences from the context for the question, then copy-paste the original text to output without any additional words. Template for output: '\n- [sentence1]\n- [sentence2] ...'" |

Examples of SelfElicit highlighting evidence and helping LM to get the correct answer.
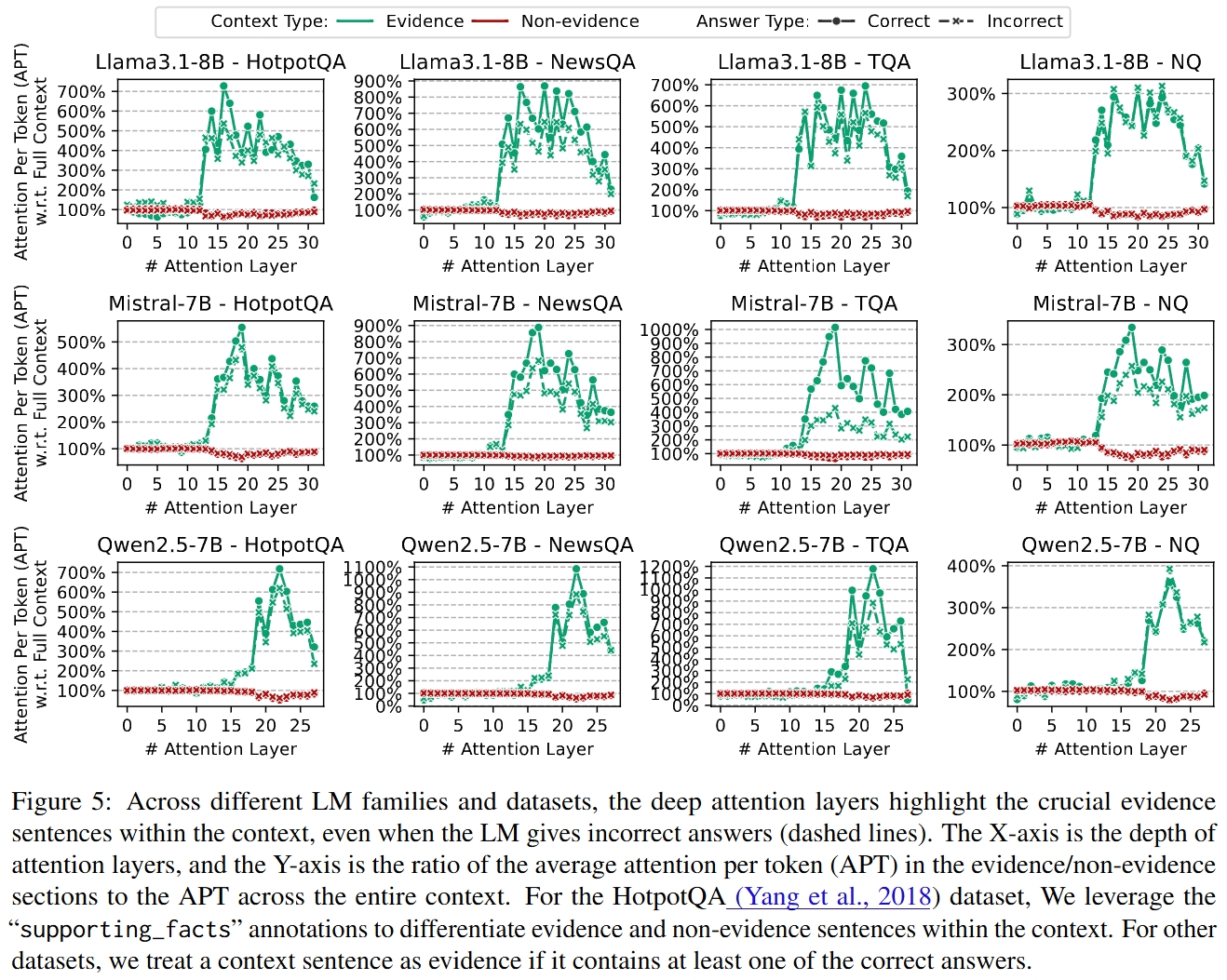
The "Evidence Reading Layers" pay high attention to the evidence sentences and exist across different LMs.
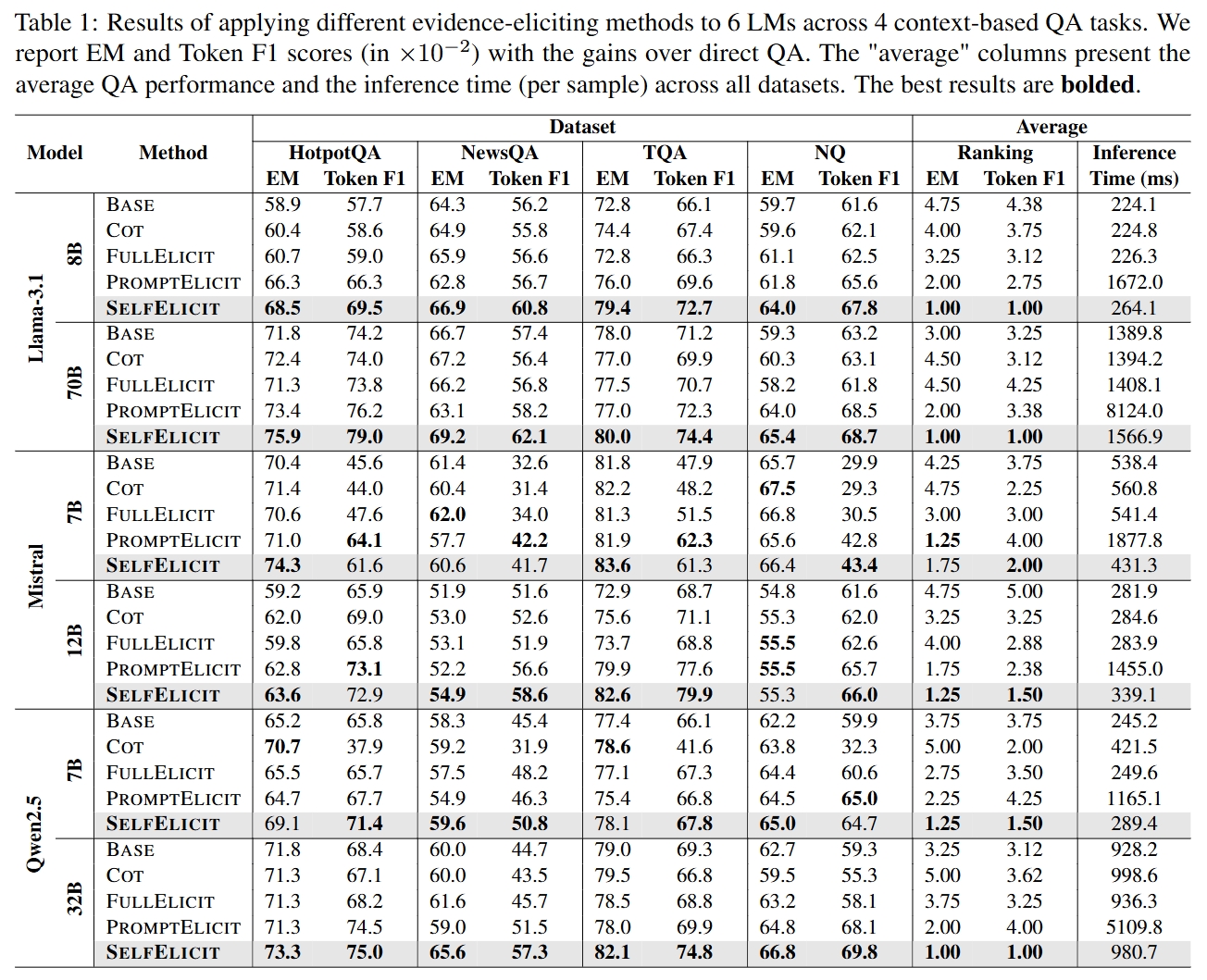
SelfElicit brings versatile performance boost on 4 context-based QA tasks with 6 different LMs.
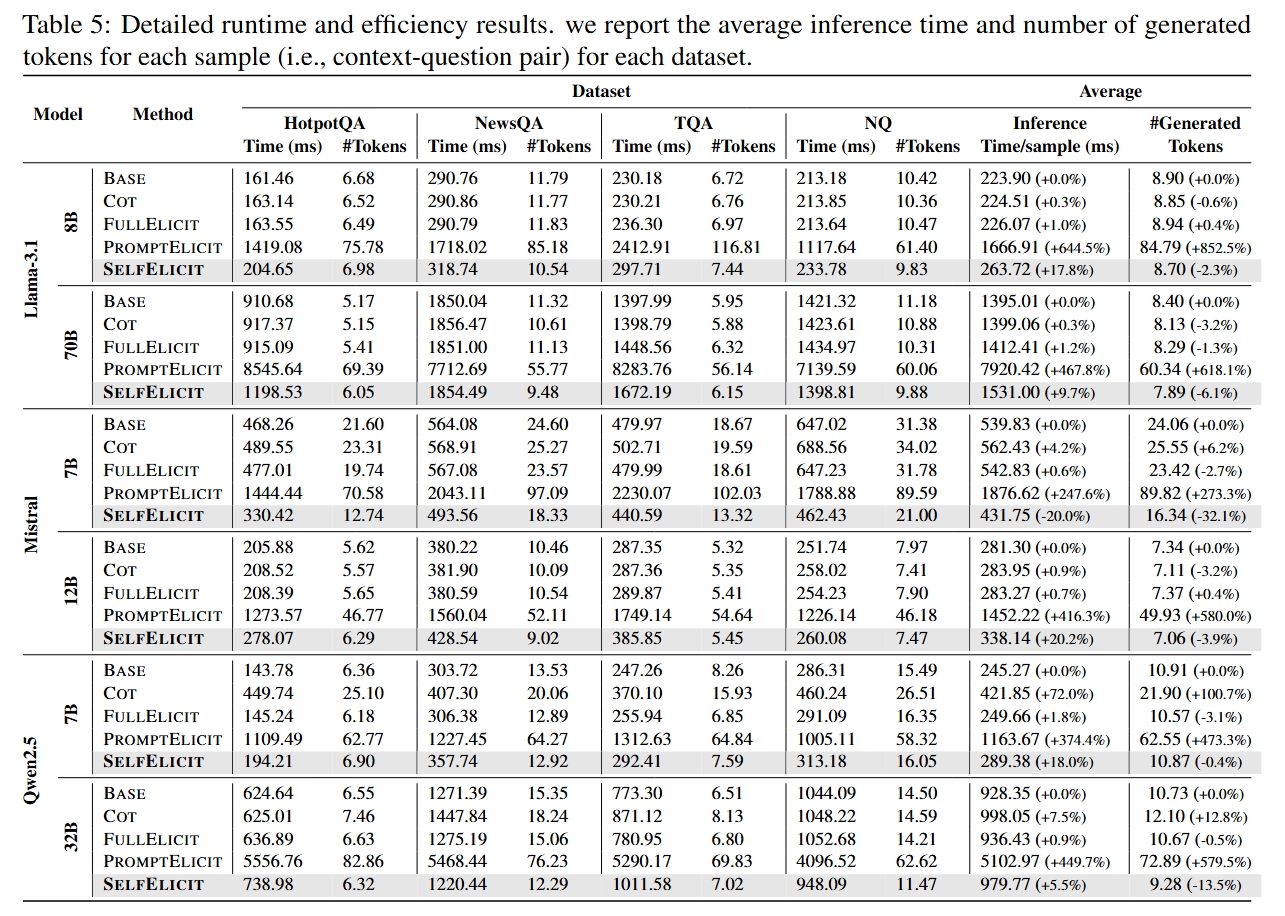 SelfElicit is computationally efficient and does not require additional training.
SelfElicit is computationally efficient and does not require additional training.
self_elicit.py: Implements the core SelfElicit algorithm and other baselines for evidence selection and context highlighting.run_experiment.ipynb: Provides a Jupyter notebook for running experiments and visualizing results.run_experiment.py: Command-line interface for running experiments with different models and datasets.config.yaml: Configuration file specifying model paths, datasets, and experiment settings.args.py: Parses command-line arguments for running the scripts.dataloader.py: Handles data loading for QA datasets (e.g., HotpotQA, TriviaQA).eval.py: Evaluation metrics for QA tasks and evidence selection accuracy.qa_agent.py: Defines the QA model interface, supporting different LM families.utils.py: Utility functions for data processing, logging, etc.
-
args:
- get_args: Function to retrieve and set up arguments for the notebook.
-
dataloader:
- load_data: Function to load datasets for the experiments.
-
utils:
- get_model_tokenizer_device: Function to load the model, tokenizer, and device (e.g., GPU or CPU) for running the experiments.
-
qa_agent:
- get_agents_dict: Function to prepare QA agent instances with different instructions.
- ContextQuestionAnsweringAgent: Class for handling context-based question answering tasks.
-
eval:
- evaluate: Function to evaluate the model's answers against the true answers using metrics like F1 score and Exact Match (EM).
-
self_elicit:
- get_answer_base: Function to get the base answer from the model.
- get_answer_cot: Function to get the answer using Chain-of-Thought (COT) reasoning.
- get_answer_fullelicit: Function to get the answer using full elicitation.
- get_answer_promptelicit: Function to get the answer using prompt elicitation.
- get_answer_selfelicit: Function to get the answer using self-elicit method.