|
13 | 13 | "source": [ |
14 | 14 | "## Introduction \n", |
15 | 15 | "\n", |
16 | | - "Raster is a type of geo-referenced data that represents phenomena occurring continuously on (or relative to) the surface of the Earth. A common example of data stored in raster format is elevation, but many other phenomena are recorded in the same way. Today many different sensors orbit the Earth on board of satellites, all collecting data in raster form.\n", |
| 16 | + "Raster data is organised in cells (pixels), each cell contains one or more values representing phenomena occurring on (or relative to) the surface of the Earth. A common example of data stored in raster format is elevation, but many other phenomena can be recorded or predicted at cell level. Today many different sensors orbit the Earth on board of satellites, all collecting data in raster form.\n", |
17 | 17 | "\n", |
18 | | - "The earliest examples of raster data were aerial photographs taken on board of aircraft that were transformed into digital format. The photograph would become a matrix of geo-referenced values - the raster. \n", |
| 18 | + "The earliest examples of raster data are aerial photographs taken on board of aircraft that are transformed into digital format. The photograph would become a matrix of geo-referenced values - the raster. \n", |
19 | 19 | "\n", |
20 | 20 | "\n", |
21 | 21 | "*Image from [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aerial_photography#/media/File:Cecil_Shadbolt_collection_-_54_-_An_aerial_view_showing_Stonebridge_Road,_Stamford_Hill,_and_Seven_Sisters_Curve,_part_of_the_Tottenham_and_Hampstead_Junction_Railway,_taken_from_2000ft.jpg)*\n", |
22 | 22 | "\n", |
23 | 23 | "\n", |
24 | 24 | "*Satellite image from [Sentinel Hub](https://www.sentinel-hub.com/blog/building-added-value-services-top-sentinel-hub)*\n", |
25 | 25 | "\n", |
26 | | - "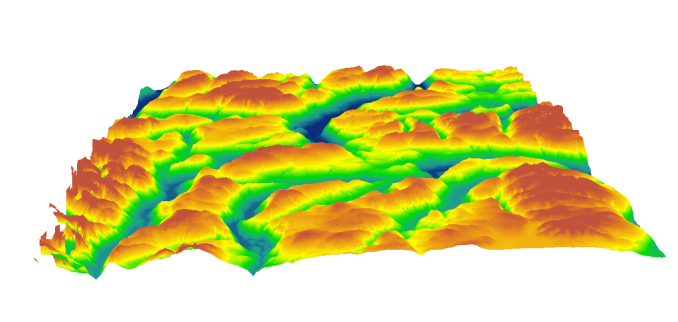\n", |
| 26 | + "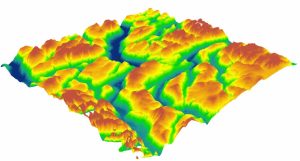\n", |
27 | 27 | "*Digital Elevation Model from [GISGeography.com](https://gisgeography.com/free-global-dem-data-sources/)*\n", |
28 | 28 | "\n", |
29 | | - "A raster captures a continuous phenomenon into a ***regular tessellation*** of space. Within each tile or cell of the raster the value of the phenomenon or variable of concern is constant. The location and size of each cell is perfectly known since the tessellation is regular. This process of collecting a continuous variable into a raster is sometimes referred to as ***discretisation***.\n", |
| 29 | + "A raster captures a continuous phenomenon into a ***regular [tessellation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tessellation)*** of space. Within each tile or cell of the raster the value of the phenomenon or variable of concern is constant. The location and size of each cell is perfectly known since the tessellation is regular. This process of collecting a continuous variable into a raster is sometimes referred to as ***discretisation***.\n", |
30 | 30 | "\n", |
31 | 31 | "\n", |
32 | 32 | "*A matrix of values composing a raster from [StackOverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/26705092/plot-a-matrix-values-as-colors)*\n", |
|
0 commit comments