You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: CONTRIBUTING.md
+7-7Lines changed: 7 additions & 7 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
1
-
# Contribute to TigerData documentation
1
+
# Contribute to Tiger Data documentation
2
2
3
-
TigerData documentation is open for contribution from all community members. The current source is in this repository.
3
+
Tiger Data documentation is open for contribution from all community members. The current source is in this repository.
4
4
5
-
This page explains the structure and language guidelines for contributing to TigerData documentation. See the [README][readme] for how to contribute.
5
+
This page explains the structure and language guidelines for contributing to Tiger Data documentation. See the [README][readme] for how to contribute.
6
6
7
7
## Language
8
8
9
-
Write in a clear, concise, and actionable manner. TigerData documentation uses the [Google Developer Documentation Style Guide][google-style] with the following exceptions:
9
+
Write in a clear, concise, and actionable manner. Tiger Data documentation uses the [Google Developer Documentation Style Guide][google-style] with the following exceptions:
10
10
11
11
- Do not capitalize the first word after a colon.
12
12
- Use code font (back ticks) for UI elements instead of semi-bold.
@@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ live in the `_partials` top-level directory. To make a new partial, create a new
100
100
101
101
## Formatting
102
102
103
-
In addition to all the [regular Markdown formatting][markdown-syntax], the following elements are available for TigerData docs:
103
+
In addition to all the [regular Markdown formatting][markdown-syntax], the following elements are available for Tiger Data docs:
104
104
105
105
- Procedure blocks
106
106
- Highlight blocks
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ See [Formatting examples][formatting] for how to use them.
113
113
114
114
## Variables
115
115
116
-
TigerData documentation uses variables for its product names, features, and UI elements in Tiger Cloud Console with the following syntax: `$VARIABLE_NAME`. Variables do not work inside the following:
116
+
Tiger Data documentation uses variables for its product names, features, and UI elements in Tiger Cloud Console with the following syntax: `$VARIABLE_NAME`. Variables do not work inside the following:
117
117
118
118
- Front matter on each page
119
119
- HTML tables and tabs
@@ -146,7 +146,7 @@ To make a documentation page more visible and clear for Google:
146
146
- Include main page keywords into the meta tags, page title, first header, and intro. These are usually the names of features described in the page. For example, for a page dedicated to creating hypertables, you can use the keyword **hypertable** in the following way:
147
147
148
148
- Title: Create a hypertable in Tiger Cloud
149
-
- Description: Turn a regular $PG table into a hypertable in a few steps, using Tiger Cloud Console.
149
+
- Description: Turn a regular Postgres table into a hypertable in a few steps, using Tiger Cloud Console.
[](https://console.cloud.timescale.com/signup)
16
+
[](https://console.cloud.timescale.com/signup)
17
17
18
18
</div>
19
19
20
-
This repository contains the current source for TigerData documentation available at https://docs.tigerdata.com/.
20
+
This repository contains the current source for Tiger Data documentation available at https://docs.tigerdata.com/.
21
21
22
-
We welcome contributions! You can contribute to TigerData documentation in the following ways:
22
+
We welcome contributions! You can contribute to Tiger Data documentation in the following ways:
23
23
24
24
-[Create an issue][docs-issues] in this repository and describe the proposed change. Our doc team takes care of it.
25
25
- Update the docs yourself and have your change reviewed and published by our doc team.
26
26
27
-
## Contribute to the TigerData docs
27
+
## Contribute to the Tiger Data docs
28
28
29
29
To make the contribution yourself:
30
30
@@ -45,9 +45,9 @@ To make the contribution yourself:
45
45
46
46
See the [Contributing guide](CONTRIBUTING.md) for style and language guidance.
47
47
48
-
## Learn about TigerData
48
+
## Learn about Tiger Data
49
49
50
-
TigerData is Postgres made powerful. To learn more about the company and its products, visit [tigerdata.com](https://www.tigerdata.com).
50
+
Tiger Data is Postgres made powerful. To learn more about the company and its products, visit [tigerdata.com](https://www.tigerdata.com).
You are charged for all active $SERVICE_SHORTs in your account, even if you are not actively using them. To reduce costs, pause or delete your unused $SERVICE_SHORTs.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: _partials/_caggs-intro.md
+8-12Lines changed: 8 additions & 12 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -1,30 +1,26 @@
1
1
import RealTimeAgg from 'versionContent/_partials/_real-time-aggregates.mdx';
2
2
3
3
In modern applications, data usually grows very quickly. This means that aggregating
4
-
it into useful summaries can become very slow. Continuous aggregates in $TIMESCALE_DB make
5
-
aggregating data lightning fast, accurate, and easy.
6
-
7
-
If you are collecting data very frequently, you might want to aggregate your
8
-
data into minutes or hours instead. For example, if an IoT device takes
4
+
it into useful summaries can become very slow. If you are collecting data very frequently, you might want to aggregate your
5
+
data into minutes or hours instead. For example, if an IoT device takes
9
6
temperature readings every second, you might want to find the average temperature
10
7
for each hour. Every time you run this query, the database needs to scan the
11
-
entire table and recalculate the average.
8
+
entire table and recalculate the average. $TIMESCALE_DB makes aggregating data lightning fast, accurate, and easy with continuous aggregates.
9
+
10
+
12
11
13
-
Continuous aggregates are a kind of hypertable that is refreshed automatically
12
+
Continuous aggregates in $TIMESCALE_DB are a kind of hypertable that is refreshed automatically
14
13
in the background as new data is added, or old data is modified. Changes to your
15
14
dataset are tracked, and the hypertable behind the continuous aggregate is
16
15
automatically updated in the background.
17
16
18
-
You don't need to manually refresh your continuous aggregates, they are
19
-
continuously and incrementally updated in the background. Continuous aggregates
20
-
also have a much lower maintenance burden than regular $PG materialized
17
+
Continuous aggregates have a much lower maintenance burden than regular $PG materialized
21
18
views, because the whole view is not created from scratch on each refresh. This
22
19
means that you can get on with working your data instead of maintaining your
23
20
database.
24
21
25
-
26
22
Because continuous aggregates are based on hypertables, you can query them in exactly the same way as your other tables. This includes continuous aggregates in the rowstore, compressed into the [columnstore][hypercore],
27
-
or [tiered to object storage][data-tiering]. You can even create [continuous aggregates on top of your continuous aggregates][hierarchical-caggs] - for an even more fine-tuned aggregation.
23
+
or [tiered to object storage][data-tiering]. You can even create [continuous aggregates on top of your continuous aggregates][hierarchical-caggs], for an even more fine-tuned aggregation.
28
24
29
25
[Real-time aggregation][real-time-aggregation] enables you to combine pre-aggregated data from the materialized view with the most recent raw data. This gives you up-to-date results on every query. <RealTimeAgg />
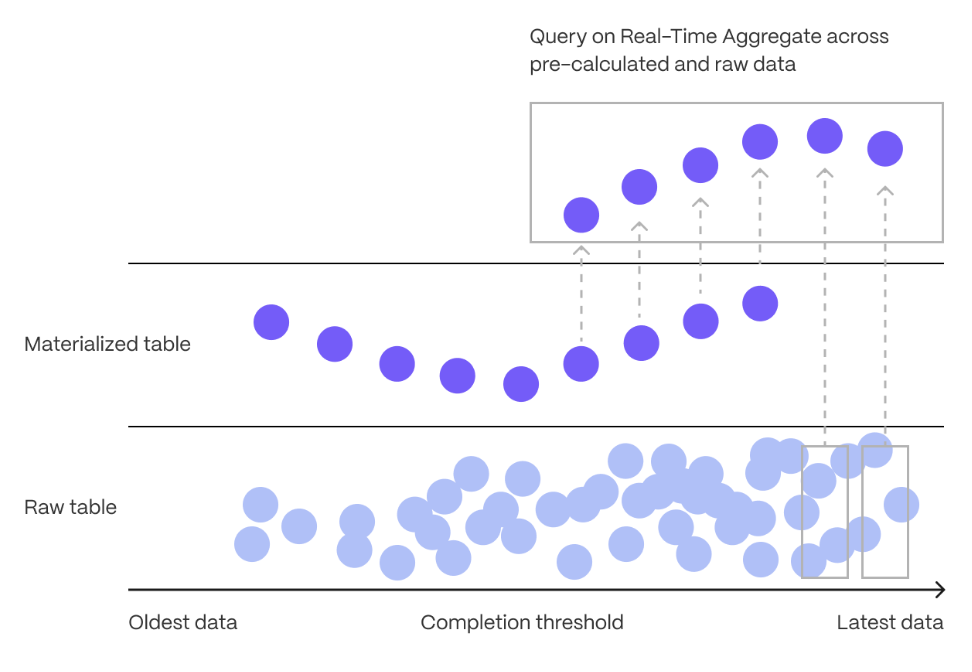
import CreateAccountConsole from "versionContent/_partials/_create-account-console.mdx";
2
+
3
+
You create a $ACCOUNT_LONG to manage your $SERVICE_SHORTs and data in a centralized and efficient manner in $CONSOLE. From there, you can create and delete $SERVICE_SHORTs, run queries, manage access and billing, integrate other services, contact support, and more.
0 commit comments