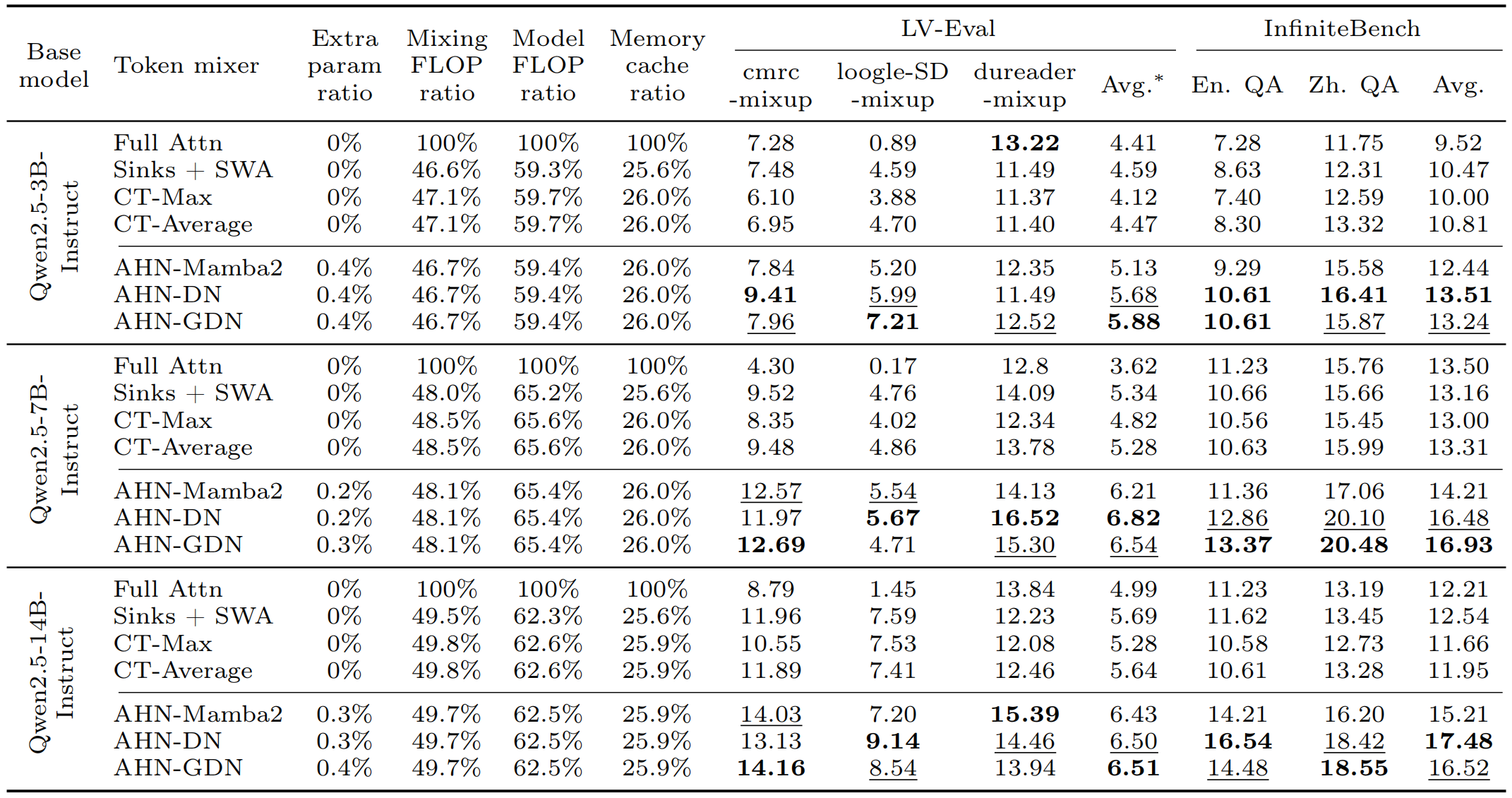
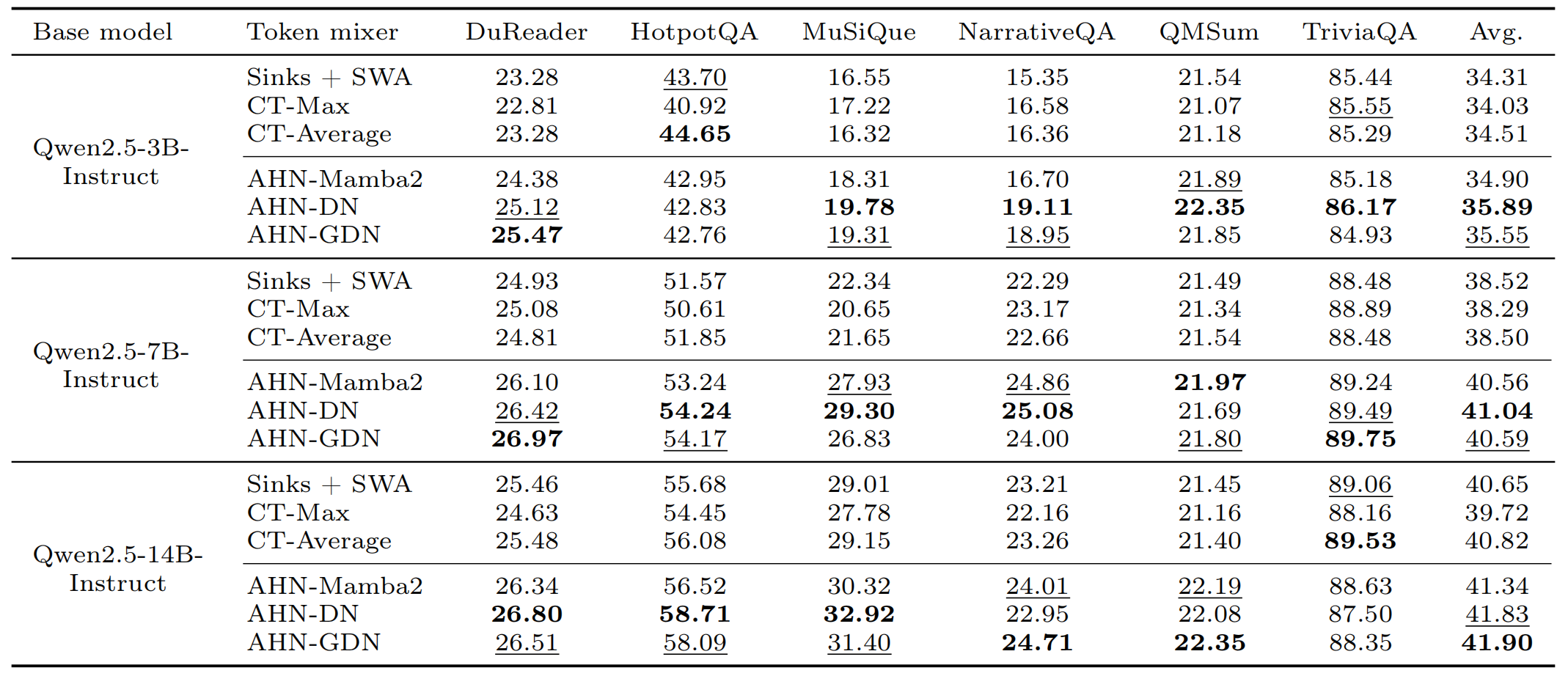
This repo provides training, inference, and evaluation instructions for the paper AHN "Artificial Hippocampus Networks for Efficient Long-Context Modeling".
- 🔥 [2025-10-08]: AHN released!.
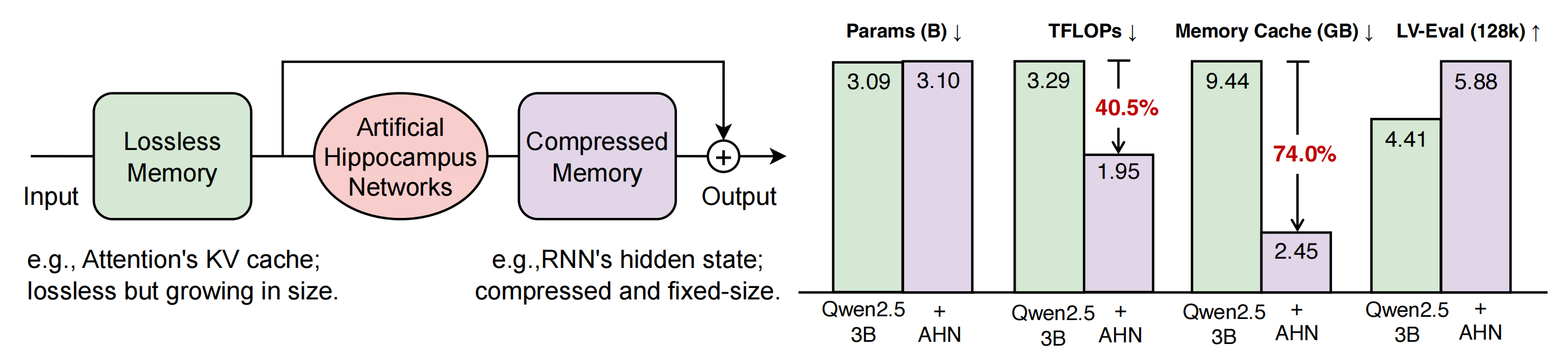
Figure 1: Artificial Hippocampus Networks (AHNs) transform lossless memory into fixed-size compressed representations for long-context modeling. Lossless memory (e.g., attention’s key-value (KV) cache) stores exact input information but grows with sequence length, making it inefficient for long sequences. In contrast, compressed memory (e.g., RNNs’ hidden state) maintains a constant size and offers fixed computational costs per input token, but this comes at the cost of information loss. To harness the benefits of both memory types, AHNs continually convert lossless memory outside the sliding attention window into compressed form. AHNs can be instantiated with any RNN-like architectures. The model then integrates both memory types to make predictions across long contexts.
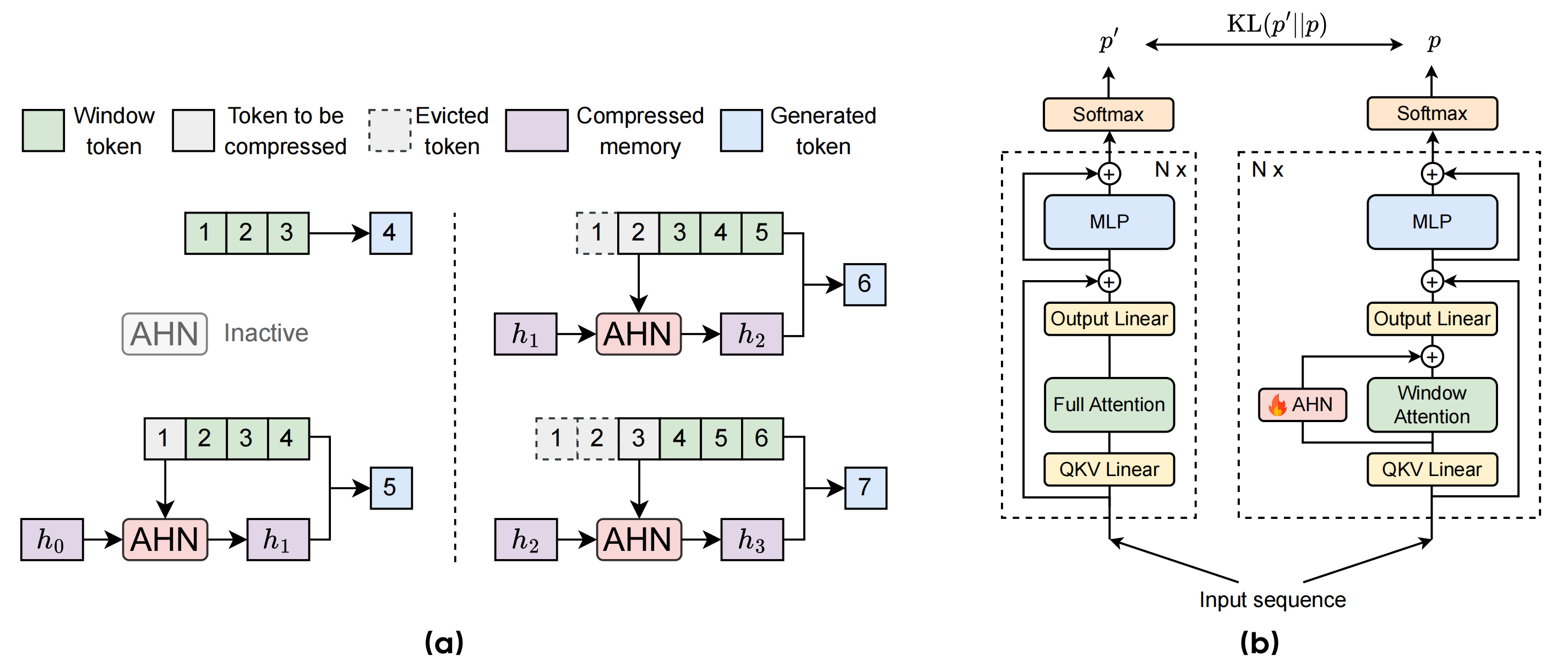
Figure 2: (a) Illustration of the model augmented with Artificial Hippocampus Networks (AHNs). In this example, the sliding window length is 3. When the input sequence length is less than or equal to the window length, the model operates identically to a standard Transformer. For longer sequences, AHNs continually compress the token outside the window into a compact memory representation. The model then utilizes both the lossless information within window, and the compressed memory to generate the next token. (b) Self-distillation training framework of AHNs based on an open-weight LLM. During training, the base LLM's weights are frozen, and only the AHNs' parameters are trained.
├── src/ # Core AHN Implementation
│ └── ahn/
│ ├── rnn/ # AHN modules in RNN-style architecture
│ └── transformer/ # Transformer backbone (e.g., Qwen2.5/3) with AHN integration
Default environment: Python 3.11, CUDA 12.4, PyTorch 2.5.1+cu124
# Install dependencies and set up AHN for training
# 1. Clone the AHN repository and move into it
git clone https://github.com/ByteDance-Seed/AHN.git
cd AHN
# 2. Install required forked libraries
pip install "git+https://github.com/Seerkfang/flash-linear-attention.git@main#egg=flash-linear-attention"
pip install "git+https://github.com/Seerkfang/LLaMA-Factory.git@main#egg=llamafactory"
# (Optional) Install the forked Mamba version if you plan to use AHN-Mamba2
# MAMBA_FORCE_BUILD=TRUE pip install "git+https://github.com/yuweihao/mamba.git"
# 3. Install AHN in editable mode with training extras
pip install -e ".[train]"| base model | AHN module | #params | checkpoint (AHN only) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | Mamba2 | 11.9M | 🤗model |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | DeltaNet | 11.8M | 🤗model |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | GatedDeltaNet | 13.0M | 🤗model |
| Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct | Mamba2 | 18.6M | 🤗model |
| Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct | DeltaNet | 18.5M | 🤗model |
| Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct | GatedDeltaNet | 21.3M | 🤗model |
| Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct | Mamba2 | 51.4M | 🤗model |
| Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct | DeltaNet | 51.1M | 🤗model |
| Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct | GatedDeltaNet | 61.0M | 🤗model |
- Merge base model and AHN weights. Example: Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct with GatedDeltaNet
# Base model (repo_id or local path)
BASE_MODEL=Qwen/Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct
# AHN-only weights (repo_id or local path)
AHN_PATH=ByteDance-Seed/AHN-GDN-for-Qwen-2.5-Instruct-3B
# Output directory for the merged model
MERGED_MODEL_PATH=./merged_ckpt/Qwen-2.5-Instruct-3B-AHN-GDN
python ./examples/scripts/utils/merge_weights.py \
--base-model $BASE_MODEL \
--ahn-path $AHN_PATH \
--output-path $MERGED_MODEL_PATHThis produces a merged model directory at MERGED_MODEL_PATH with both base and AHN parameters.
- Run inference on a single GPU (example: GPU 0)
PROMPT="When was the concept of AI introduced?"
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python ./examples/scripts/inference.py \
--model $MERGED_MODEL_PATH \
--prompt "$PROMPT"Example: Training Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct with GatedDeltaNet as the AHN module on ChatQA2, using a default global batch size of 128 across 32 GPUs (~700 steps):
bash ./examples/scripts/train_qwen2.5_3b_ahn_gdn.shKey arguments:
-
--model_name_or_path- Choose base model
- Examples:
Qwen/Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct,Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct
-
--dataset- Specify dataset for training
- Default:
chatqa2
-
--loss_type- Specify the loss function
- Options:
kl,ce
-
--ahn_implementation- Select the AHN memory module
- Allowed values:
GatedDeltaNet,DeltaNet,Mamba2
-
--ahn_position- Control where AHN modules are inserted
- Options:
prefix,random
-
--sliding_window_type- Define the sliding window strategy
- Options:
fixed,random
-
--save_ahn_only- Whether or not to save AHN only
- Options:
True,False
-
--filter_len- Filter training data by sequence length (e.g., keep samples longer than the length,
288)
- Filter training data by sequence length (e.g., keep samples longer than the length,
-
--cutoff_len- Set the cutoff sequence length (e.g.,
24576)
- Set the cutoff sequence length (e.g.,
Quick debug on a single GPU (GPU 0):
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 bash ./examples/scripts/debug.shFor full evaluation details, please the evaluation instructions.
- Yunhao Fang: [email protected]
- Weihao Yu (corresponding author): [email protected]
BibTeX:
@article{fang2025artificial,
title={Artificial hippocampus networks for efficient long-context modeling},
author={Fang, Yunhao and Yu, Weihao and Zhong, Shu and Ye, Qinghao and Xiong, Xuehan and Wei, Lai},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2510.07318},
year={2025}
}We thank Shi Guang, Haoqi Fan, Tianle Cai, Deyao Zhu, Tenglong Ao, Shilong Liu, Ge Zhang, Wenhao Huang, and Liang Xiang for valuable discussions. We would like to thank the developers of 🤗 transformers, LLaMA-Factory, flash-linear-attention and mamba for their open-source contributions that made this project possible.